TOP > MANAGEMENT SYSTEM > RESEACH & DEVELOPMENT
Aiming For A R&D Division That Remains At the Forefront of Industry

Nippon Ketjen is developing a variety of advanced technologies associated with hydrotreating catalyst through the joint research program with universities and public research organizations. These programs range over a wide field of technologies and include constituent techniques for catalyst characterization, oil analysis and the elucidation of key reaction mechanisms by tracing model reactions. We also address upgrading technologies for the coming further imbalance between supply and demand of heavy oil products.
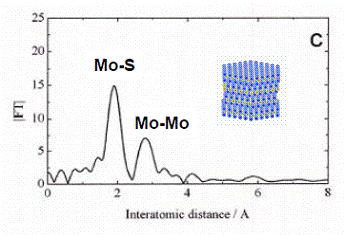
Identification of active sites where catalytic reactions occur is essential for developing conceptual design of new catalysts. Hydrotreating catalysts are usually activated by sulfurizing active metal oxides loaded on supports, which means that it is important to evaluate the detailed chemical structures of the corresponding active metal sufides. The figure on the right shows an example of the Mo K-edge radial distribution function of sulfurized catalyst determined by Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure spectroscopy. This technique provides us with insists about the dispersion of active metals and the formation of active sites, and consequently strongly helps us develop the design of advanced catalysts.
Evaluation of intrinsic activity requires determining how much of contaminants including sulfur and nitrogen in feedstock are removed and elucidating how molecular structures in the feed stock change in the course of practical hydrotreating. The figure on the left shows an example of the progression in asphaltene hydrogenation by residue hydrotreating. It is easily seen that both quantity and quality of asphaltene molecules change by the specialized functions of HDM and HDS catalysts, respectively.
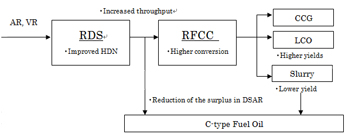
Nippon Ketjen takes the impact on overall refinery objectives into account when developing hydrotreating catalysts. The figure on the left shows the flow scheme of residue hydrotreating and the following residue fluid catalytic cracking (RFCC) as an example. We are aiming to achieve further great synergy between these processes through the development of residue hydrotreating catalysts that will enhance the efficiency of the downstream RFCC process.















